Hilton Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
The analytical framework of Porter’s Five Forces developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] explains five separate forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are represented in Figure 1 below:
Figure 1. Hilton Porter’s Five Forces
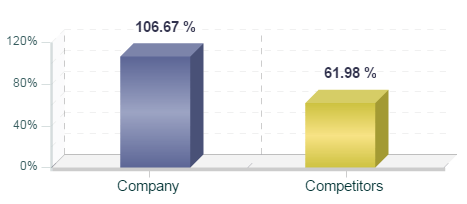
Rivalry among existing firms in premium segment hotel industry is fierce. Hilton Hotels and Resorts competes with Marriott, Sheraton, Hyatt Regency, Radisson Blu, Renaissance, Westin, Sofitel and other premium segment hotel chains in the global marketplace. As a result of massive investments into various aspects of the service provision during the past few years, Hilton enjoyed greater income growths compared to the competition. Specifically, as it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Net Income in the 1 quarter 2016 grew year on year by 106.67 %, faster than average growth of its competitors.
Figure 2. Income growth differences between Hilton Worldwide and its competitors[1]
Bargaining power of Hilton suppliers is low. Hilton Worldwide purchases from more than 4000 suppliers globally [2] and the bargaining power of most suppliers is low due to the lack of uniqueness of products and services supplied. Moreover, the importance of order volume for Hilton suppliers is paramount and there is no supplier switching costs for Hilton on most cases. Hilton runs Supplier Diversity Program that ensures purchasing from, and the development of, socially diverse suppliers. Accordingly, the program provides an additional competitive ground for socially diverse suppliers compared to other supplier groups.
Threat of substitute products or services in hotel industry is not significant. Direct substitutes for staying in Hilton hotels includes people staying in the homes of friends and relatives and people renting apartments for short periods of time. However, arrangement of these options can be time-consuming and associated with a great deal of hassle. Hotel industry is also faced with technology-fuelled indirect substitution such as video conferencing, since this form of communication can eliminate the need to travel to another place and stay in a hotel…
Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Report contains a full version of Hilton Porter’s Five Forces Analysis. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Value Chain Analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Hilton. Moreover, the report contains analysis of Hilton’s marketing strategy, discusses leadership and organizational structure and addresses the issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Source: CSI Market, Available at: http://csimarket.com/stocks/compet_glance.php?code=HLT
[2]Hilton Worldwide 2014-2015 Corporate Responsibility Report
[1] Porter, M. (1979) “How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy” Harvard Business Review